Josephus Problem

There are N people standing in a circle waiting to be executed. The counting out begins at some point in the circle and proceeds around the circle in a fixed direction. In each step, a certain number of people are skipped and the next person is executed. The elimination proceeds around the circle (which is becoming smaller and smaller as the executed people are removed), until only the last person remains, who is given freedom.
Given the total number of persons N and a number k which indicates that k-1 persons are skipped and the kth person is killed in a circle. The task is to choose the person in the initial circle that survives.
Examples:
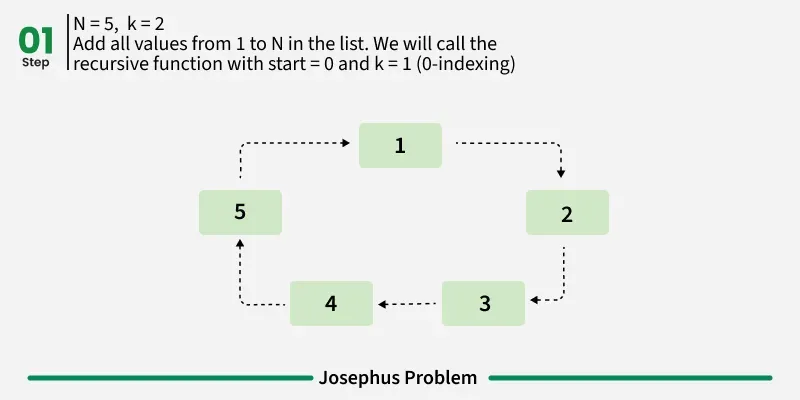
Input: N = 5 and k = 2
Output: 3
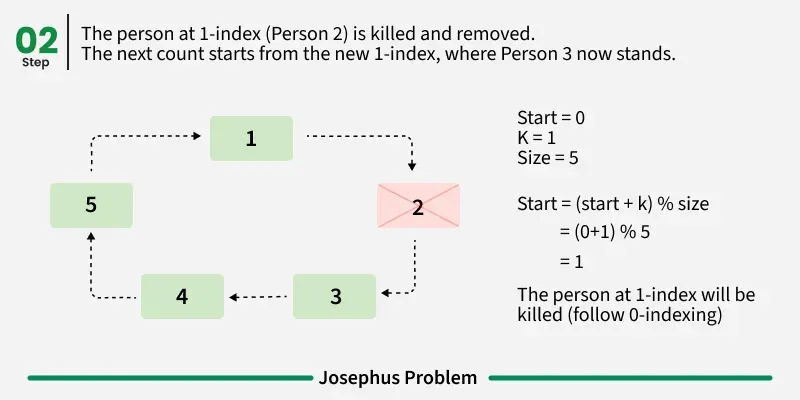
Explanation: Firstly, the person at position 2 is killed,
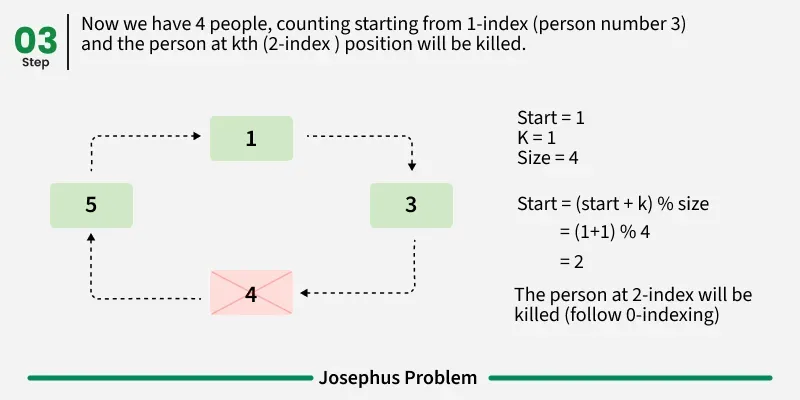
then the person at position 4 is killed, then the person at position 1 is killed.
Finally, the person at position 5 is killed. So the person at position 3 survives.Input: N = 7 and k = 3
Output: 4
Explanations: The persons at positions 3, 6, 2, 7, 5, and 1 are killed in order,
and the person at position 4 survives.Input: N = 6 and k = 2
Output: 5
Explanation: The persons at positions 2, 4, 6, 3, and 1 are killed in order, and the person at position 5 survives.
[Approach – 1] Solving Josephus problem using List:
The simple approach is to create a list and add all values from 1 to N to it. Create a recursive function that takes a list, start (position at which counting will start), and k ( number of people to be skipped) as an argument.
- If the size of the list is one i.e. only one person left then return this position.
- Otherwise, start counting the k person in a clockwise direction from starting position and remove the person at the kth position.
- Now the person at the kth position is removed and now counting will start from this position. This process continues till only one person is left.
Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
- Create a vector person and push all the values from 1 to N in person.
- Recursively eliminate the index element
- Erase the element on the position index.
- Call for (index + k)% size of person.
- If size of person = 1, return person[i].
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void Josh(vector<int> person, int k, int index)
{
// Base case , when only one person is left
if (person.size() == 1) {
cout << person[0] << endl;
return;
}
// find the index of first person which will die
index = ((index + k) % person.size());
// remove the first person which is going to be killed
person.erase(person.begin() + index);
// recursive call for n-1 persons
Josh(person, k, index);
}
int main()
{
int n = 14; // specific n and k values for original
// josephus problem
int k = 2;
k--; // (k-1)th person will be killed
int index
= 0; // The index where the person which will die
vector<int> person;
// fill the person vector
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
person.push_back(i);
}
Josh(person, k, index);
}
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void Josh(List<Integer> person, int k, int index)
{
// Base case , when only one person is left
if (person.size() == 1) {
System.out.println(person.get(0));
return;
}
// find the index of first person which will die
index = ((index + k) % person.size());
// remove the first person which is going to be killed
person.remove(index);
// recursive call for n-1 persons
Josh(person, k, index);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String [] args)
{
int n = 14; // specific n and k values for original
// josephus problem
int k = 2;
k--; // (k-1)th person will be killed
int index
= 0; // The index where the person which will die
List<Integer> person = new ArrayList<>();
// fill the person vector
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
person.add(i);
}
Josh(person, k, index);
}
}
# Python code for Josephus Problem
def Josh(person, k, index):
# Base case , when only one person is left
if len(person) == 1:
print(person[0])
return
# find the index of first person which will die
index = ((index+k)%len(person))
# remove the first person which is going to be killed
person.pop(index)
# recursive call for n-1 persons
Josh(person,k,index)
# Driver Program to test above function
n = 14 # specific n and k values for original josephus problem
k = 2
k-=1 # (k-1)th person will be killed
index = 0
# fill the person vector
person=[]
for i in range(1,n+1):
person.append(i)
Josh(person,k,index)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static void Josh(List<int> person, int k, int index)
{
// Base case , when only one person is left
if (person.Count == 1) {
Console.WriteLine(person[0]);
return;
}
// find the index of first person which will die
index = ((index + k) % person.Count);
// remove the first person which is going to be killed
person.RemoveAt(index);
// recursive call for n-1 persons
Josh(person, k, index);
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int n = 14; // specific n and k values for original
// josephus problem
int k = 2;
k--; // (k-1)th person will be killed
int index
= 0; // The index where the person which will die
List<int> person = new List<int>();
// fill the person vector
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
person.Add(i);
}
Josh(person, k, index);
}
}
function Josh( person , k , index) {
// Base case , when only one person is left
if (person.length == 1) {
console.log(person[0]);
return;
}
// find the index of first person which will die
index = ((index + k) % person.length);
// remove the first person which is going to be killed
if (index > -1) {
person.splice(index, 1);
}
// recursive call for n-1 persons
Josh(person, k, index);
}
// Driver code
var n = 14; // specific n and k values for original
// josephus problem
var k = 2;
k--; // (k-1)th person will be killed
var index = 0; // The index where the person which will die
var person = [];
// fill the person vector
for (var i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
person.push(i);
}
Josh(person, k, index);
Output
13
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N), For recursion stack
[Approach – 2] Solving Josephus problem iteratively
Illustration:



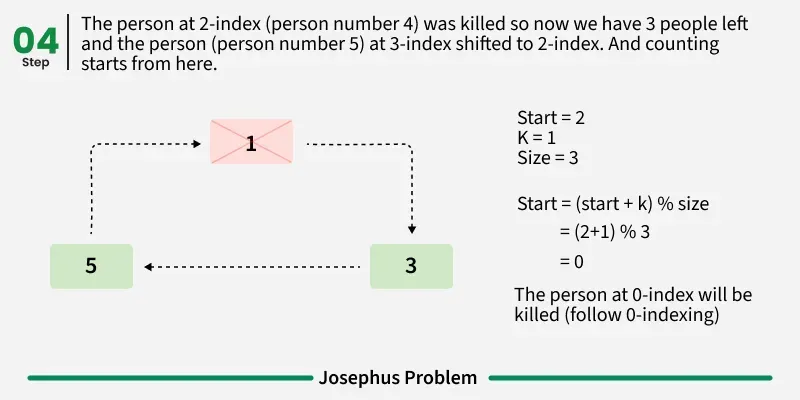

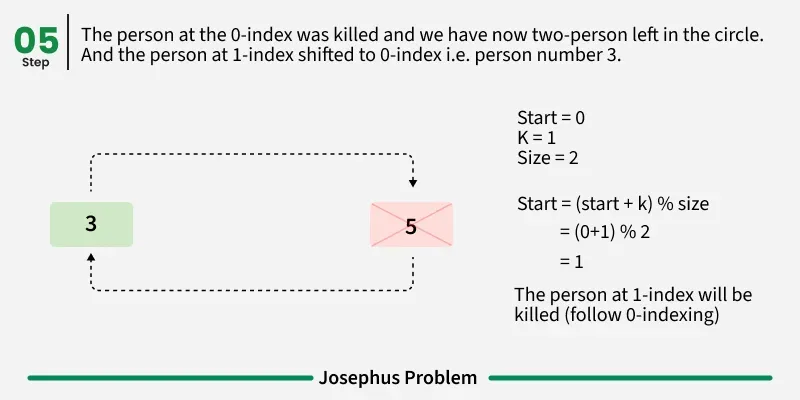

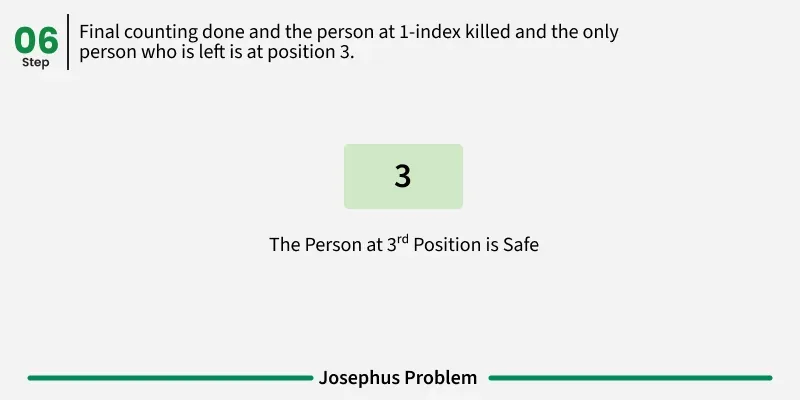

Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
- Initialize variables num, cnt, and cut with 1, 0, and 0 respectively and an array arr[] of size N with the initial value set as 1.
- Run a while loop till cnt < N:
- Run a while loop till num is less than equal to k.
- Increment cut by one and take modulo by N
- If arr[cut] = 1 increment num by one.
- Set num = 1, arr[cut] = 0 and increment cnt and cut by one and cut = cut % n;
- Run a while loop till arr[cut] = 0 and increment cut by one.
- Run a while loop till num is less than equal to k.
- Return cnt + 1 as the required answer.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Josephus(int, int);
int Josephus(int n, int k)
{
k--;
int arr[n];
// Makes all the 'n' people alive by
// assigning them value = 1
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = 1;
}
int cnt = 0, cut = 0,
// Cut = 0 gives the sword to 1st person.
num = 1;
// Loop continues till n-1 person dies.
while (cnt < (n - 1)) {
// Checks next (kth) alive persons.
while (num <= k) {
cut++;
// Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
cut = cut % n;
if (arr[cut] == 1) {
// Updates the number of persons
// alive.
num++;
}
}
// Refreshes value to 1 for next use.
num = 1;
// Kills the person at position of 'cut'
arr[cut] = 0;
// Updates the no. of killed persons.
cnt++;
cut++;
// Checks and resolves overflow of Index.
cut = cut % n;
// Checks the next alive person the
// sword is to be given.
while (arr[cut] == 0) {
cut++;
// Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
cut = cut % n;
}
}
// Output is the position of the last
// man alive(Index + 1);
return cut + 1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 14, k = 2;
cout << Josephus(n, k);
return 0;
}
// Java code to implement the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 14, k = 2;
System.out.println(Josephus(n, k));
}
public static int Josephus(int n, int k)
{
k--;
int arr[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = 1; // Makes all the 'n' people alive by
// assigning them value = 1
}
int cnt = 0, cut = 0,
num
= 1; // Cut = 0 gives the sword to 1st person.
while (
cnt
< (n
- 1)) // Loop continues till n-1 person dies.
{
while (num
<= k) // Checks next (kth) alive persons.
{
cut++;
cut = cut
% n; // Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
if (arr[cut] == 1) {
num++; // Updates the number of persons
// alive.
}
}
num = 1; // refreshes value to 1 for next use.
arr[cut] = 0; // Kills the person at position of
// 'cut'
cnt++; // Updates the no. of killed persons.
cut++;
cut = cut % n; // Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
while (arr[cut]
== 0) // Checks the next alive person the
// sword is to be given.
{
cut++;
cut = cut
% n; // Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
}
}
return cut
+ 1;
}
}
def Josephus(n, k):
k -= 1
arr = [0]*n
for i in range(n):
arr[i] = 1 # Makes all the 'n' people alive by
# assigning them value = 1
cnt = 0
cut = 0
num = 1 # Cut = 0 gives the sword to 1st person.
while (cnt < (n - 1)):
# Loop continues till n-1 person dies.
while (num <= k):
# Checks next (kth) alive persons.
cut += 1
cut = cut % n # Checks and resolves overflow
# of Index.
if (arr[cut] == 1):
num+=1 # Updates the number of persons
# alive.
num = 1 # refreshes value to 1 for next use.
arr[cut] = 0 # Kills the person at position of 'cut'
cnt += 1 # Updates the no. of killed persons.
cut += 1
cut = cut % n # Checks and resolves overflow of Index.
while (arr[cut] == 0):
# Checks the next alive person the
# sword is to be given.
cut += 1
cut = cut % n # Checks and resolves overflow
# of Index.
return cut + 1 # Output is the position of the last
# man alive(Index + 1)
# Driver Code
n, k = 14, 2 #map (int, input().splut())
print(Josephus(n, k))
# This code is contributed by ShubhamSingh
// C# code to implement the above approach
using System;
using System.Linq;
public class GFG{
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 14, k = 2;
Console.Write(Josephus(n, k));
}
public static int Josephus(int n, int k)
{
k--;
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = 1; // Makes all the 'n' people alive by
// assigning them value = 1
}
int cnt = 0, cut = 0,
num = 1; // Cut = 0 gives the sword to 1st person.
while (
cnt
< (n - 1)) // Loop continues till n-1 person dies.
{
while (num <= k) // Checks next (kth) alive persons.
{
cut++;
cut = cut % n;
// Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
if (arr[cut] == 1)
{
num++; // Updates the number of persons
// alive.
}
}
num = 1; // refreshes value to 1 for next use.
arr[cut]
= 0; // Kills the person at position of 'cut'
cnt++; // Updates the no. of killed persons.
cut++;
cut = cut
% n; // Checks and resolves overflow of Index.
while (arr[cut]
== 0) // Checks the next alive person the
// sword is to be given.
{
cut++;
cut = cut % n; // Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
}
}
return cut + 1; // Output is the position of the last
// man alive(Index + 1);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shubham Singh
// Javascript code to implement the above approach
let n = 14, k = 2;
console.log(Josephus(n, k));
function Josephus(n, k)
{
k--;
let arr = new Array(n);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Makes all the 'n' people alive by
// assigning them value = 1
arr[i] = 1;
}
// Cut = 0 gives the sword to 1st person.
let cnt = 0, cut = 0,
num = 1;
// Loop continues till n-1 person dies.
while (cnt < (n - 1))
{
// Checks next (kth) alive persons.
while (num <= k)
{
cut++;
cut = cut % n;
// Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
if (arr[cut] == 1)
{
// Updates the number of persons
// alive.
num++;
}
}
// refreshes value to 1 for next use.
num = 1;
arr[cut] = 0; // Kills the person at position of 'cut'
// Updates the no. of killed persons.
cnt++;
cut++;
// Checks and resolves overflow of Index.
cut = cut % n;
// Checks the next alive person the
// sword is to be given.
while (arr[cut] == 0)
{
cut++;
// Checks and resolves overflow
// of Index.
cut = cut % n;
}
}
// Output is the position of the last
// man alive(Index + 1);
return cut + 1;
}
Output
13
Time Complexity: O(n2)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
[Approach – 3] Solving Josephus Problem in Linear Time and Constant Space
Follow the below steps:
- Initialize variables i and ans with 1 and 0 respectively.
- Run a while loop till i <= N:
- Update ans with (ans + k) % i.
- Increment i by 1.
- Return ans + 1 as the required answer.
// C++ code to Implement Josephus Problem
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Josephus(int N, int k)
{
// Initialize variables i and ans with 1 and 0
// respectively.
int i = 1, ans = 0;
// Run a while loop till i <= N
while (i <= N) {
// Update the Value of ans and Increment i by 1
ans = (ans + k) % i;
i++;
}
// Return required answer
return ans + 1;
}
// main function
int main()
{
int N = 14, k = 2;
cout << Josephus(N, k) << endl;
return 0;
}
// C Program to Implement Josephus Problem
#include <stdio.h>
int Josephus(int N, int k)
{
// Initialize variables i and ans with 1 and 0
// respectively.
int i = 1, ans = 0;
// Run a while loop till i <= N
while (i <= N) {
// Update the Value of ans and Increment i by 1
ans = (ans + k) % i;
i++;
}
// Return required answer
return ans + 1;
}
// main function
int main()
{
int N = 14, k = 2;
printf("%d", Josephus(N, k));
return 0;
}
// Java code to Implement Josephus Problem
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static int Josephus(int N, int k) {
// Initialize variables i and ans with 1 and 0 respectively.
int i = 1, ans = 0;
// Run a while loop till i <= N
while (i <= N) {
// Update the Value of ans and Increment i by 1
ans = (ans + k) % i;
i++;
}
// Return required answer
return ans + 1;
}
// main function
public static void main (String[] args) {
int N = 14, k = 2;
int ans = Josephus(N, k);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
# python code to implement Josephus problem
# Josephus function which will take
# two parameter N and K, number of people and positions respectively
# return the position of person survives
def Josephus(n, k):
# initialize two variables i and ans
i = 1
ans = 0
while(i <= n):
# update the value of ans
ans = (ans + k) % i
i += 1
# returning the required answer
return ans + 1
# driver code
# let
n = 14
k = 2
result = Josephus(n, k)
print(result)
// C# code to Implement Josephus Problem
using System;
class GFG
{
public static int Josephus(int N, int k)
{
// Initialize variables i and ans with 1 and 0 respectively.
int i = 1, ans = 0;
// Run a while loop till i <= N
while (i <= N)
{
// Update the Value of ans and Increment i by 1
ans = (ans + k) % i;
i++;
}
// Return required answer
return ans + 1;
}
// main function
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int N = 14, k = 2;
int ans = Josephus(N, k);
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
}
// driver code
let n = 14, k = 2;
console.log(Josephus(n,k));
// Josephus function
// return the position of last man survives
function Josephus(n, k)
{
let i = 1, ans = 0;
while(i <= n ){
// update the value of ans
ans = (ans + k) % i;
i++;
}
return ans + 1;
}
Output
13
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
[Approach – 4] Solving Josephus Problem using Recursion
The problem has the following recursive structure. josephus(n, k) = (josephus(n – 1, k) + k-1) % n + 1 and josephus(1, k) = 1
After the first person (kth from the beginning) is killed, n-1 persons are left. Make recursive call for Josephus(n – 1, k) to get the position with n-1 persons. But the position returned by Josephus(n – 1, k) will consider the position starting from k%n + 1. So make adjustments to the position returned by Josephus(n – 1, k).
// C++ code to implement the idea
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Recursive function to implement the Josephus problem
int josephus(int n, int k)
{
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
// The position returned by josephus(n - 1, k)
// is adjusted because the recursive call
// josephus(n - 1, k) considers the
// original position k % n + 1 as position 1
return (josephus(n - 1, k) + k - 1) % n + 1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 14;
int k = 2;
cout << "The chosen place is " << josephus(n, k);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int josephus(int n, int k)
{
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
/* The position returned by josephus(n - 1, k) is
adjusted because the recursive call josephus(n -
1, k) considers the original position
k%n + 1 as position 1 */
return (josephus(n - 1, k) + k - 1) % n + 1;
}
// Driver Program to test above function
int main()
{
int n = 14;
int k = 2;
printf("The chosen place is %d", josephus(n, k));
return 0;
}
// Java code for Josephus Problem
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int josephus(int n, int k)
{
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
/* The position returned by josephus(n - 1, k)
is adjusted because the recursive call
josephus(n - 1, k) considers the original
position k%n + 1 as position 1 */
return (josephus(n - 1, k) + k - 1) % n + 1;
}
// Driver Program to test above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 14;
int k = 2;
System.out.println("The chosen place is "
+ josephus(n, k));
}
}
# Python code for Josephus Problem
def josephus(n, k):
if (n == 1):
return 1
else:
# The position returned by
# josephus(n - 1, k) is adjusted
# because the recursive call
# josephus(n - 1, k) considers
# the original position
# k%n + 1 as position 1
return (josephus(n - 1, k) + k-1) % n + 1
# Driver Program to test above function
n = 14
k = 2
print("The chosen place is ", josephus(n, k))
// C# code for Josephus Problem
using System;
class GFG {
static int josephus(int n, int k)
{
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
/* The position returned
by josephus(n - 1, k) is
adjusted because the
recursive call josephus(n
- 1, k) considers the
original position k%n + 1
as position 1 */
return (josephus(n - 1, k) + k - 1) % n + 1;
}
// Driver Program to test above
// function
public static void Main()
{
int n = 14;
int k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("The chosen "
+ "place is " + josephus(n, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
// Javascript code for Josephus Problem
function josephus(n, k)
{
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
/* The position returned
by josephus(n - 1, k) is
adjusted because the
recursive call josephus(n
- 1, k) considers the
original position k%n + 1
as position 1 */
return (josephus(n - 1, k)
+ k-1) % n + 1;
}
let n = 14;
let k = 2;
console.log("The chosen " + "place is " + josephus(n, k));
<?php
// PHP code for
// Josephus Problem
function josephus($n, $k)
{
if ($n == 1)
return 1;
else
/* The position returned by
josephus(n - 1, k) is
adjusted because the
recursive call josephus
(n - 1, k) considers the
original position k%n + 1
as position 1 */
return (josephus($n - 1, $k) +
$k - 1) % $n + 1;
}
// Driver Code
$n = 14;
$k = 2;
echo "The chosen place is ", josephus($n, $k);
?>
Output
The chosen place is 13
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n) the space used in recursion call stack
Related Article: Josephus problem | Set 2 (A Simple Solution when k = 2)